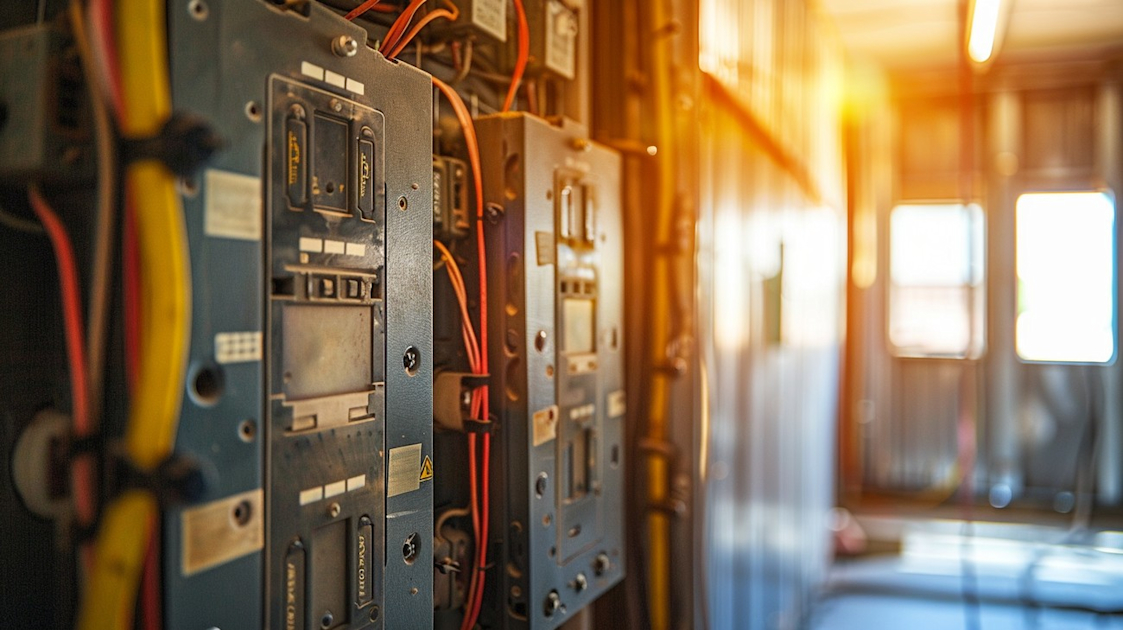
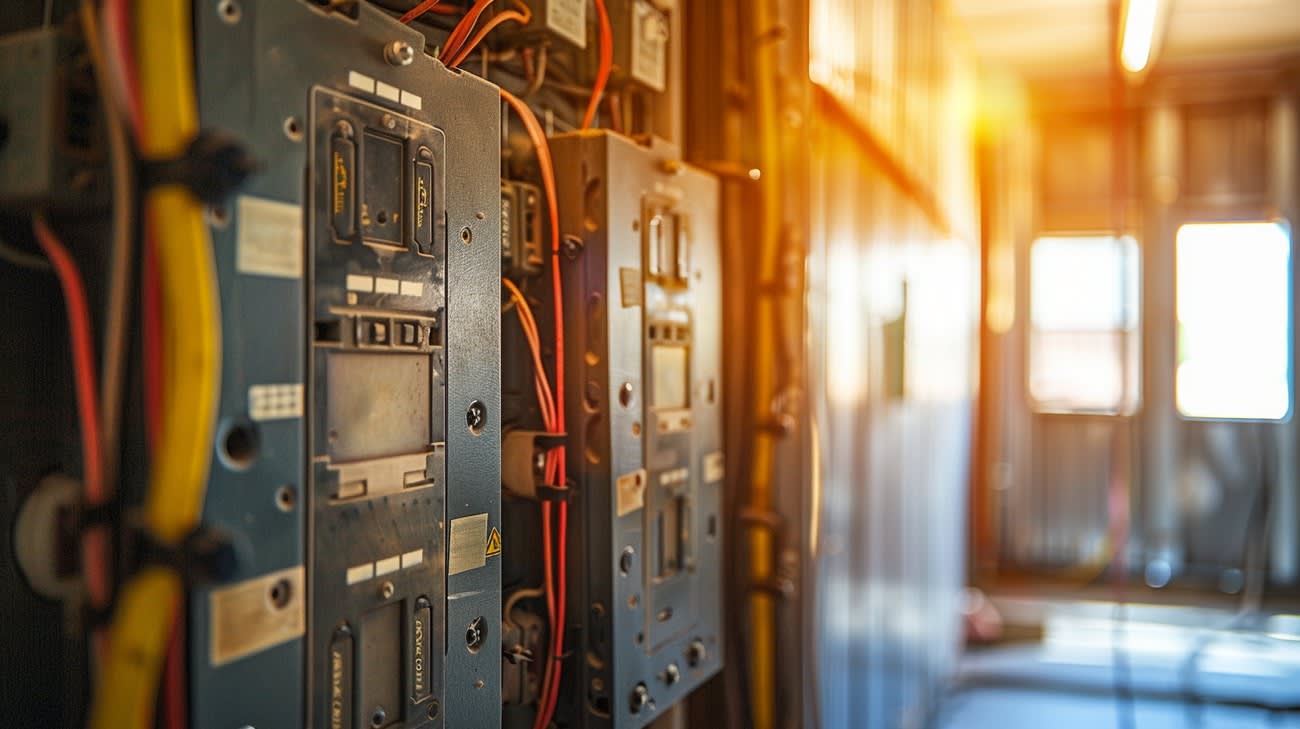
The realm of electrical systems can sometimes feel complex, especially when you're dealing with elements like the main breaker and subpanel. Understanding how these components work, where they fit into your home's electrical architecture, and what benefits they offer is crucial. This article delves deep into the topic to provide clarity and insight into these indispensable elements of your home's power distribution system.
What is a Main Breaker?
A main breaker is essentially the heart of your electrical system. It's the large switch you find in your main electrical panel that controls the power flow to your entire house. Its primary function is to offer a failsafe, cutting off electricity when the current exceeds safe limits. Without it, excess electricity could lead to severe damage or even a fire.
Key Functions of a Main Breaker
- Power Control: Shuts off the power supply in case of overload.
- Safety: Protects against potential fire hazards by regulating excess electrical flow.
- Centralized Switching: Allows you to disconnect the entire home from the electrical supply for maintenance or emergencies.
Understanding the Subpanel
While the main breaker is analogous to a general manager overseeing everything, the subpanel is like having a department manager to handle specific sections of the operation. A subpanel is an extension of the main panel, offering additional circuit spaces and helping distribute electrical power throughout your home more efficiently.
Key Functions of a Subpanel
- Extension of Circuitry: Provides additional circuit capacity, especially useful in expansions or specific areas requiring more power.
- Localized Control: Offers electrical control for a specific area, reducing the need to access the main panel frequently.
- Load Management: Helps distribute electrical load more evenly across circuits, optimizing performance and avoiding overloads.
Differences Between a Main Breaker and Subpanel
Understanding the main distinctions between a main breaker and a subpanel helps clarify their roles and implications in your home's electrical system.
Capacity and Location
- Main Breaker: Located in the main service panel, it manages the entire home's electrical capacity.
- Subpanel: Found in various locations to address localized power needs; does not independently handle the entire home's load.
Functionality
- Main Breaker: Controls and disconnects the house's entire electrical flow.
- Subpanel: Extends the main panel's reach and provides power to specific sections without affecting the main supply.
When to Use a Main Breaker
Understanding when to focus on the main breaker is crucial for maintaining safety and functionality in your home.
- Power Surge Management: When large appliances cause frequent power surges.
- System Upgrades: During significant electrical system overhauls or new installations.
- Safety Checks: Routine maintenance or when introducing a substantial new electrical load.
When to Utilize a Subpanel
There are specific scenarios where a subpanel becomes immensely beneficial, promoting efficiency and organization within your electrical system.
- Home Additions: Installing a subpanel can accommodate extra electricity load in new spaces like garages or workshops.
- Improved Circuit Organization: Maintain a clutter-free and organized main panel.
- Dedicated Area Management: Use when a particular area of your home (like a basement or pool area) requires its own circuit set.
Installation Considerations
Installing either a main breaker or a subpanel involves a degree of complexity, requiring thoughtful planning and often professional involvement.
Main Breaker Installation
- Professional Assessment: Always have a licensed electrician examine your current setup.
- Plan for Future Growth: Consider the need for additional capacity in the long run.
- Adhere to Code: Ensure the installation meets all local electrical regulations and standards.
Subpanel Installation
- Assess Load Requirements: Determine the specific load needs of the area it will service.
- Strategic Placement: Choose a location that minimizes the length of additional wiring required.
- Optimize Circuit Use: Plan circuits to optimize usage and prevent potential overloads.
Safety Considerations
Ensuring safety when dealing with either the main breaker or subpanel should be a top priority. Here’s a brief rundown of essential safety tips:
- Regular Inspections: Schedule routine checks to catch potential issues before they escalate.
- Clear Labels: Clearly label all breakers and circuits to prevent confusion during emergencies or maintenance.
- Keep Free from Obstruction: Ensure access to panels is never blocked to facilitate quick action when needed.

Main Breaker vs Subpanel: Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a main breaker in an electrical system?
The main breaker in an electrical system acts as the central point of control for the entire electrical setup in a building. It is typically located in the main electrical panel and is responsible for safeguarding the circuit by controlling the flow of electricity from the utility company into the building. When too much current flows through the electrical system, the main breaker will trip, cutting off the electricity to prevent damage to the system or a potential fire risk. This breaker is primarily installed to protect the entire electrical system from overloads or short circuits, ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical use throughout the property.
How does a subpanel differ from a main breaker panel?
A subpanel is essentially a smaller service panel that branches off from the main breaker panel. It acts as an extension of the main electrical service panel and is used to distribute power to specific areas or heavy-load equipment in a building. Unlike the main breaker, a subpanel does not have its own meter; it is fed by a feeder line from the main panel and is used to create neater, more organized electrical distribution. The subpanel adds convenience by allowing you to control electricity distribution to select areas without accessing the main panel. This setup is useful when managing electrical loads in different parts of a home or an addition with separate power needs.
Why is a subpanel necessary in some homes or buildings?
A subpanel is necessary in situations where an addition to the home requires a concentrated amount of power or when the main panel has reached its circuit limit. Expanding electrical capacity via a subpanel helps to streamline the control of power distribution to specific parts of a building, such as garages, workshops, or secondary suites. It reduces the need for long, convoluted wiring leading to the main breaker panel and allows easy access to circuit breakers for maintenance or resets. By adding a subpanel, you enhance the safety and efficiency of the electrical system, making it easier to isolate power in parts of the property for repairs or renovations.
How do you install a subpanel in relation to the main breaker?
Installing a subpanel requires a careful approach to ensure it safely connects to the main breaker panel. First, you need to identify a suitable location for the subpanel, ideally near the area with the significant electrical load. Begin by running a feeder cable from the main breaker panel to your chosen location. This cable connects the subpanel to the main panel, providing it with electricity. Before proceeding, make sure to shut off the main power for safety. Once the feeder cable is attached, connect the subpanel to the main panel's grounding system to ensure proper operation. Upon installation, make sure every connection is secure and in compliance with local electrical codes and standards.
Can a subpanel have its own main breaker?
Yes, a subpanel can have its own main breaker, and this is often recommended for convenience and safety. Including a main breaker in the subpanel allows easy shutoff of power to the subpanel if maintenance or an emergency arises. This feature is especially useful if the subpanel is located a significant distance from the main panel, as it provides a localized point to cut the power without needing to travel back to the main breaker. Having a main breaker in the subpanel also adds an extra layer of safety because it protects the subpanel from overcurrent, similar to the main breaker for the primary electrical system.
Does the main breaker size affect the subpanel installation?
The size of the main breaker does indeed affect subpanel installation, primarily because it determines the maximum electrical load the system can handle. When installing a subpanel, it’s crucial to ensure that the total load on the main breaker, including the subpanel, does not exceed its capacity. Assess the current load on the main panel and calculate whether adding a subpanel will fit within the available capacity. If the main breaker is undersized for the additional load, it can lead to frequent tripping or overheating, which poses a safety hazard. Proper load calculation ensures that both the main breaker and the subpanel operate efficiently without causing undue stress on the electrical system.
How many subpanels can be installed from a single main breaker panel?
The number of subpanels you can install from a single main breaker panel largely depends on the capacity of the main breaker and the electrical load demands of your home or building. Generally, as long as the total electrical load from all the subpanels, along with any existing circuits, does not exceed the main breaker's capacity, multiple subpanels can be installed. However, practical considerations include available space in the main panel for additional circuit breakers and the adequacy of your current electrical setup to handle the additional load safely. Consulting a qualified electrician for a load calculation is always recommended to ensure your system remains efficient and code-compliant.
What safety precautions should be taken when working with a main breaker and subpanel?
Safety is paramount when working with a main breaker or subpanel, given the risks associated with electricity. Always turn off power at the main breaker before beginning any work on the subpanel or main panel to prevent accidental shock or injury. Use insulated gloves and tools rated for electrical work to reduce the risk of electric shock. Familiarize yourself with the layout of the electrical system, ensuring you know which circuits you are working on. It's crucial to follow the local electrical code and standards, as improper installation can lead to serious safety hazards, including electrical fires. If unsure, seek help from a licensed electrician to ensure that the installation is done safely and correctly.
Comparison
Key Features Comparison
| Feature | Main Breaker | Subpanel |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Central point that cuts power | Extends existing circuits |
| Capacity | Handles entire home’s load | Handles limited load, specific zones |
| Installation | Primary panel connected to utility | Secondary, needs existing main panel |
| Overcurrent Protection | Primary protection for home | Secondary, usually less robust |
| Expansibility | Limited by entire panel capacity | Adds circuits without overloading |
Main breakers are the heart of a home's electrical system, designed to control power distribution efficiently. Subpanels serve as extensions, allowing additional circuits, making them ideal for home expansions, garages, or workshops.
Performance Differences
Main Breaker: The main breaker acts as a safeguard for the overall home, preventing electrical overload and potential hazards by cutting off power if the current demand exceeds safe levels. This single point of control is essential for homes needing robust, comprehensive coverage.
Subpanel: Subpanels provide flexibility and convenience without interference with the main circuit. They offer localized control over specific areas, contributing to load management, reducing wire runs, and thus improving performance by preventing strain on a singular system.
Performance-wise, the main breaker offers the advantage of comprehensive protection. However, a subpanel enhances the performance of your electrical system by allowing for focused power distribution, enhancing efficiency in targeted locations and facilitating future expansion.
Price Comparison
| Component | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Main Breaker | $100 - $300 |
| Subpanel | $50 - $150 |
The cost of a main breaker is usually higher, reflecting its critical role and capacity to handle a full home's electrical needs. Conversely, subpanels are more affordable, as they are secondary and support specific areas.
However, prices can vary based on capacity, brand, and additional features such as smart technology integration. Installation costs will also vary depending on the complexity and existing infrastructure.
Best Use Cases for Each
Main Breaker:
- Ideal for new home construction or complete system overhauls where centralized control and comprehensive protection are paramount.
- Necessary in situations requiring coordination with utility companies for connection and disconnection procedures.
- Suitable for homes requiring high-capacity handling due to numerous high-energy appliances or electrical devices.
Subpanel:
- Perfect for adding new circuits in a detached garage, workshop, or outbuilding without overhauling the entire electrical system.
- Effective in home additions where extending the original wiring and capacity is needed.
- Useful for distributing power specifically to high-demand areas, like kitchens or entertainment setups, without taxing the main panel.
Bottom Line Recommendation
When choosing between a main breaker and a subpanel, consider the scope and purpose of your project. For whole-home protection and maximum control, a main breaker is indispensable. Conversely, subpanels provide optimal solutions for extended or enhanced electrical distribution in specific areas. They both have unique advantages depending on the needs and layout of your home or building. The decision should be informed by specific project goals, existing infrastructure, and budget allowances.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between main breaker vs subpanel is crucial for effectively managing your electrical system, especially when considering your home’s power needs, additions, or upgrades. Whether you're expanding your garage or simply ensuring you're protected against overloads, knowing when to use a main breaker versus a subpanel can help you make informed decisions and keep your home safe and efficient.
At Sagan Electric, we’re here to help homeowners in Sacramento, CA, navigate these electrical choices with ease. If you're considering an upgrade or have questions about your existing setup, feel free to reach out to us. We’re always ready to provide expert advice, schedule a consultation, or offer a free estimate tailored to your specific needs. Let’s ensure your electrical system is up to par so you can enjoy peace of mind at home.
Tags: electrical panel, circuit breaker, electrical wiring,








