Understanding Line and Load in Electrical Wiring
When it comes to the electrical wiring of your home or office, it's crucial to know the difference between line and load. Despite being often used interchangeably, line and load represent separate components in electrical systems and feature in both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power supplies. In this article, we share with you everything there is to comprehend about line vs load, an essential concept in ensuring electrical safety and system efficiency in domestic and commercial settings.
Line in Electrical Circuits
The term "line" in electrical circuits designates the wire or wires that supply power from the main power source to electrical devices. Within a wiring system, the line is also commonly referred to as "live" or "hot." It's the point from which electricity flows into a circuit.
Identifying the Line Wire
Recognizing the line wire in a circuit system is key to maintaining safety while handling electrical systems. In a standard two-wire setup, the line wire is typically black or red and is always responsible for carrying power from the source to the device. In a three-wire setup seen in larger electrical appliances, the line wire remains the colored one, usually red or black, apart from the white neutral wire and the green or bare ground wire.
Load in Electrical Circuits
The "load" in an electrical circuit refers to the device or component that consumes the supplied electricity to perform its function. This could be a light bulb, a refrigerator, a computer, or any other electrically powered device. The load wire carries power from the line to power up or down the device.
Identifying Load Wires
Similar to the line wire, it's essential to identify load wires for safety reasons. In a standard wiring configuration, the load wire is typically the one returning to the source after powering the load or device. In a simple circuit, the load wire runs from the device back to the power source and is often color-coded as white.
Importance of Understanding "Line Vs Load"
The line vs load distinction is indispensable for a variety of reasons, from installation projects, ensuring safety, to troubleshooting and maintenance of electrical systems.
-
Correct Installation: When installing outlets, switches, or circuit breakers, it is crucial to connect wires correctly. This avoids possible short circuits or damage to electrical components.
-
Safety: Knowing which is the line (live wire), reducing the risk of electric shock when handling circuits.
-
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Understanding the line and load concept allows for more straightforward diagnosis of problems in a circuit. This helps prevent unnecessary repairs or replacements.
Considerations for GFCI and AFCI Devices
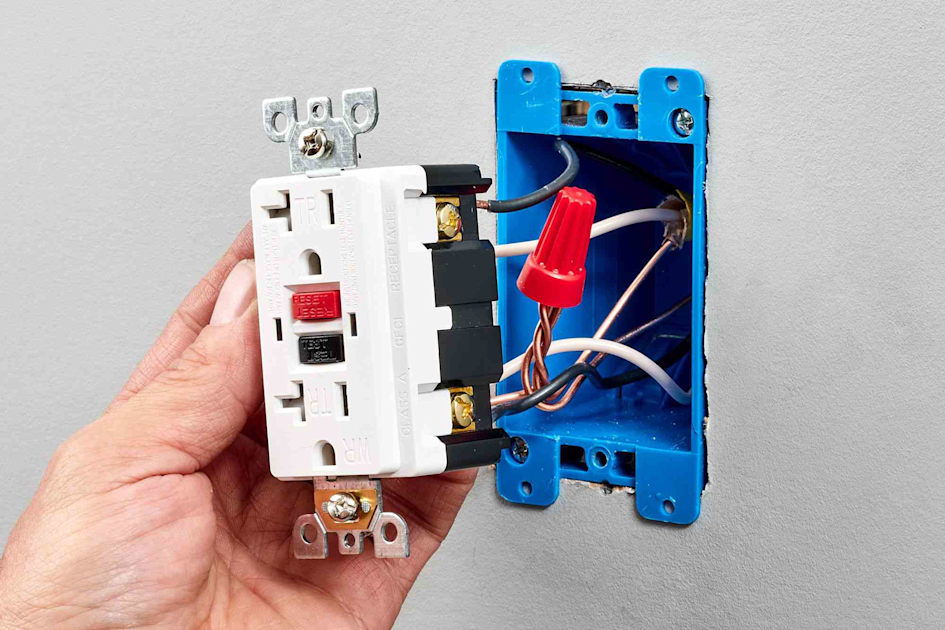
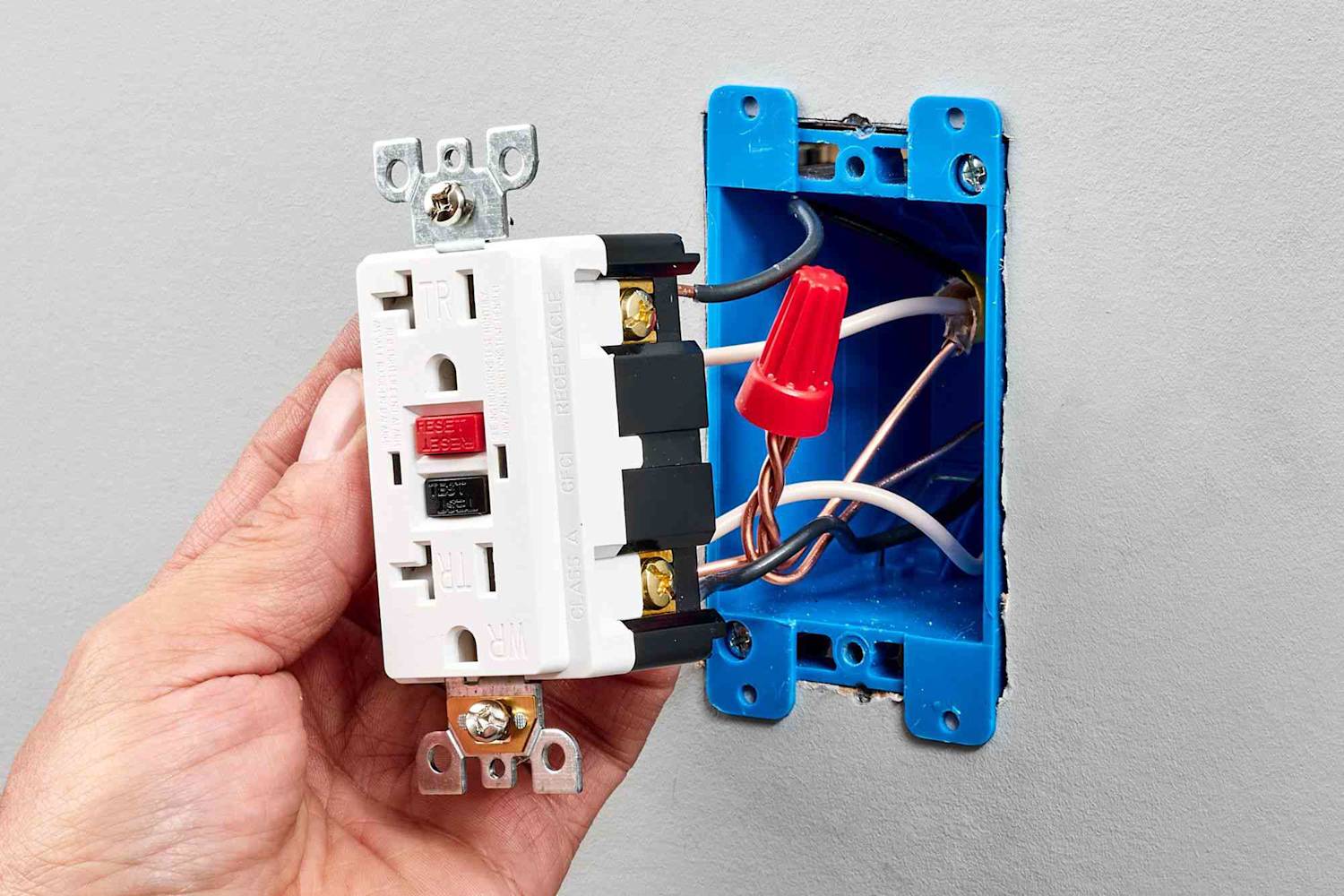
One particular area where the understanding of line vs load becomes critical is in Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) devices. These special types of circuit breakers have marked line and load terminals to differentiate the input power source from the output to the devices. Wiring these devices incorrect can result in failure or ineffective protection from ground and arc faults.
GFCI and AFCI Installation
To install a GFCI or AFCI, the line wires (usually black and white) should be connected to the 'line' terminals on the device. The 'load' terminals should then be connected to the wires that will carry power to the other devices in the circuit. This is typically a set of black and white wires similar to the line wires. An additional wire, usually green or bare, is connected to the ground terminal.
Understanding the line vs load concept not only helps ensure safe and successful wiring projects but also leads to a more comprehensive understanding of how electrical systems work. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or an electrical professional, this knowledge certainly goes a long way in avoiding electrical mishaps and ensuring appropriate troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions on Line vs Load
What are the Differences Between Line and Load in Electrical Terms?
Line and load refer to key concepts in electrical circuitry. The line is the side of the electrical circuit that brings in power, also known as the 'hot wire.' Its role is to carry electricity from the power source into the device or an electrical circuit. On the other hand, load refers to elements in the electrical circuit utilizing the power, like the light bulbs or appliances. This is also known as the 'neutral wire,' which carries electricity away from the device or circuit.
Why is it Important to Distinguish Between Line and Load?
Knowing the difference between line and load is vital to the operation and safety of your electrical systems. Errors in line and load placement can lead to system malfunctions or potential safety hazards. Also, understanding which is the line and the load will make it easier to troubleshoot problems with your electrical system.
Can the Line and Load be Interchanged?
No, the line and load should not be interchanged. The line and load wires have specific duties in an electrical circuit. The line, as previously mentioned, carries power into the device or circuit while the load carries it away. Interchanging them could cause system malfunctions or pose a safety hazard.
What Happens if Line and Load are Reversed?
If line and load are reversed in an electrical circuit, the device attached to the circuit may not work. This mistake can also damage the device or pose a dangerous fire risk due to incorrect electrical flow.
What Color are Line and Load Wires?
In most electrical circuits, the line or "hot" wire is typically black or red, whereas the load or "neutral" wire is often white. However, note that color coding can vary, so it's always a good idea to consult a professional if you're uncertain.
What Does 'Line Side' and 'Load Side' Mean?
The "line side" and "load side" are terminologies used to distinguish between the input (line) and output (load) ends of a circuit breaker or switch. The line side refers to the wiring carrying electricity from the source, while the load side refers to the part of the circuit that's delivering power to a certain load like a light, appliance, etc.
How Can I Identify the Line and Load in a Circuit?
Carefully examining the terminals can often reveal which is the line and which is the load. You may see labels, such as "L" for the line and "NL" for the load. However, always consult an electrician if you are unsure or uncomfortable making this identification.
Why Does the Line Wire Always Need to be Connected First?
The line wire always needs to be connected first to provide a safe control of power throughout the electrical system. By connecting the line first, you ensure that the safety systems within a switch, outlet, or relay have power to function properly before supplying power to the load. This prioritization helps reduce the risk of electrical shock and unsafe operations of devices.
Do Circuit Breakers Have a Line and Load Side?
Yes, circuit breakers do have a line and load side. The line side is where the breaker connects to the main power supply. On the other hand, the load side is where the breaker connects to the circuits in your home or workplace. This is important as it helps protect your electrical system from overloads or short circuits.
What is the Meaning of Load Line in a Ship?
In a non-electrical context, a load line on a ship is also known as the Plimsoll line. This line signifies the maximum safe level to which a ship may be loaded for specific water temperatures and types. The varying load capabilities are indicated by a series of lines that mark the absolute limit a vessel may safely reach under differing conditions. The system helps in ensuring the ship's stability while at sea.
Pros and Cons of Line vs Load
Pros of Line Wiring
Dependability
-
With line wiring, the power comes directly from the source, resulting in a robust supply that is not affected by other devices. This leads to a highly reliable power connection that is less likely to fail compared to load side connections.
-
This method of wiring can be more secure and dependable because it does not necessitate the sharing of power with other devices or circuits. It is less likely to be affected by the electrical demands or fluctuations in other circuits.
Increased Safety
-
Since line wiring connects directly to the source, it reduces the risk of electrical overloads and potential hazards as the power is not being divided among multiple devices or circuits.
-
If the circuit breaker is adequately sized and installed, the risk of electrical fires is significantly reduced.
Cons of Line Wiring
Complexity of Installation
-
Line wiring is typically more complicated and time-consuming to install than load wiring as it may require a direct connection to the service panel.
-
The installation process can be complicated by the necessity for a higher degree of electrical knowledge and expertise, and therefore may necessitate the hiring of a professional electrician.
Cost
-
As a result of its complexity, the cost of installing line wiring can be higher than load wiring.
-
The need for a professional electrician to ensure the proper installation can also add to the cost.
Pros of Load Wiring
Configuration Flexibility
-
A load side connection offers greater flexibility in terms of circuit configurations, as it allows for multiple devices or circuits to be connected to a single line connection.
-
This type of wiring is particularly beneficial in premises that utilize a large number of electrical devices or in cases where power needs to be distributed among multiple circuits.
Ease of Installation
-
The installation process for load wiring is usually simpler, making it a more convenient option for homeowners and DIY enthusiasts.
-
Unlike line wiring, load wiring may not require a direct connection to the service panel.
Cons of Load Wiring
Potential for Overloading
-
As load wiring splits the source power over multiple devices or circuits, there is an increased risk of overloading the circuit if the load exceeds the line capacity.
-
This could lead to frequent circuit breaker trips or, in the worst-case scenario, potential fire hazards.
Reduced Dependability
-
Any issue in the line connection could affect multiple devices or circuits, resulting in a less reliable source of power.
-
Similarly, high demand from one device could potentially impact the performance of others connected to the same circuit, known as a "voltage drop."
Both line and load wiring have their respective pros and cons. Line wiring is typically more dependable and safe but can be more complex and expensive to install. Conversely, load wiring provides greater flexibility and ease of installation but can be less reliable and pose an increased risk of overloading. Choosing between line wiring and load wiring is entirely dependent on the specific electrical requirements, available resources, and individual needs.
Summary
Understanding the concept of "line vs load" is crucial in the world of electrical projects. These two terms refer to the power supply and the electrical device to which it is connected. The line is the side of an electrical device that is directly connected to a power source, like an electrical outlet or circuit breaker, whereas, the load side is where all your devices or load are connected to. This concept helps in taking necessary safeguards against potential electrical hazards.
Whether you are an experienced electrician, or a homeowner dabbling in DIY repairs, the knowledge of "line vs load" offers an essential insight into the safe execution of electrical work. When correctly understood and implemented, distinguishing the line from the load can prevent a plethora of electrical mishaps, including short circuits or fire hazards. So, it is essential to become familiar with these terms and their proper usage.
The "line vs load" concept allows us to understand the flow of electricity better. It provides us with a deeper comprehension of how electricity travels from the main power supply, through our outlets, and to our devices. It's important to have a good understanding of this concept for correctly installing electrical wiring or circuit breakers. It is also an important piece of knowledge to increase the efficiency and longevity of our appliances.
About Sagan Electric
Welcome to Sagan Electric, your reliable and dedicated full-service electrical company in Sacramento, CA. Ever since our inception, we've been committed to providing high-quality electrical services with unflinching professionalism, trust, and integrity. Whether it's a simple electrical repair or an extensive electrical installation, our team of skilled and experienced electricians always gets the job done right. Want to know more about us and our services? Click here and let's spark up a conversation.
Tags: electrical wiring, circuits, line vs load,