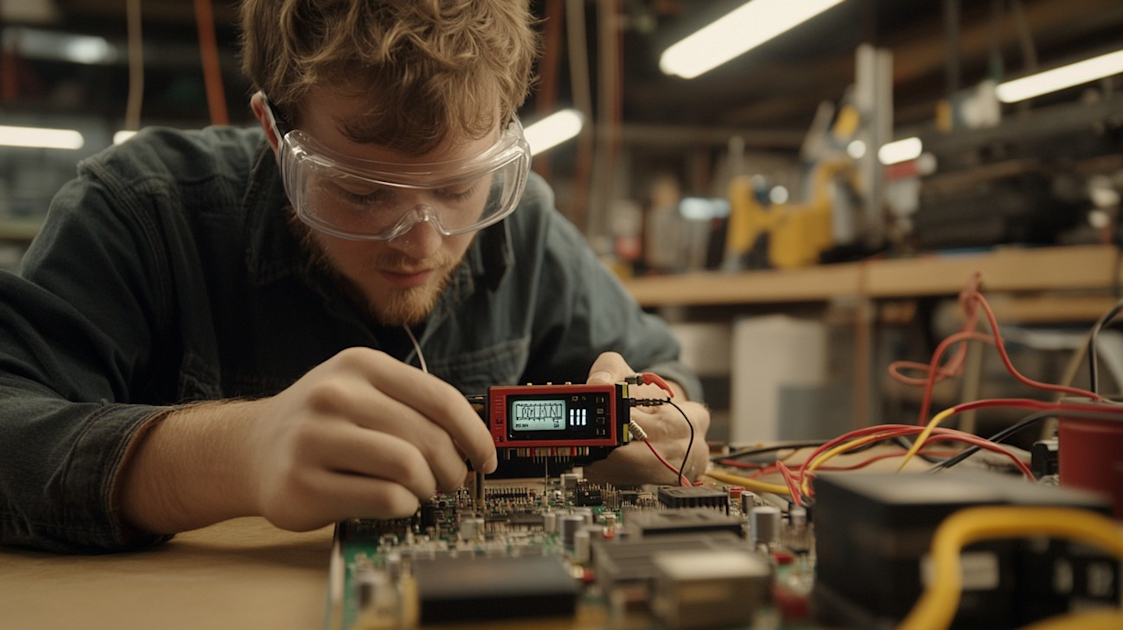
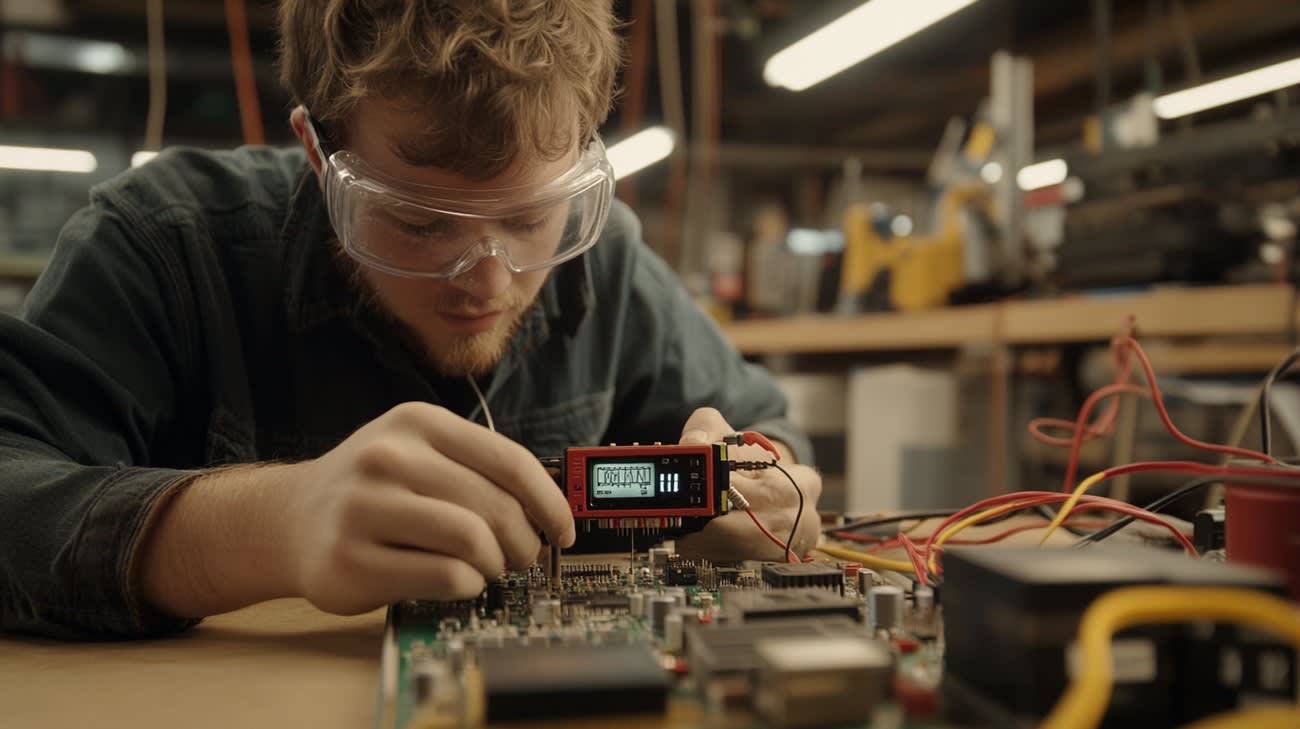
You may come across situations where you need to determine whether a capacitor in your electronic device is functioning properly. Herein, we present an informative guide on how to test a capacitor. This actionable guide is full of details and technical insights to help you master this skill with absolute ease.
Understanding The Capacitor
Capacitors, the vital components of any electronic or electrical device, store electrical energy temporarily and discharge it when necessary. They essentially help smooth the output of power supplies. But how to identify when they are faulty? Testing is the key, and we're here to tell you how.
Necessary Tools to Test a Capacitor
Before testing a capacitor, ensure you have the following tools on hand:
- A digital multimeter or an analog meter
- A capacitor discharge tool
It's essential to use the right tools to get accurate results. Plus, bear in mind to wear safety glasses when working with electronics, as a basic safety measure.
Checking a Capacitor Using a Multimeter
Testing a capacitor using a multimeter is a common method. Here’s a step-by-step process on how to carry out this task.
Prepare the Capacitor for Testing
Before starting the testing process, it is necessary to discharge the capacitor to safeguard against accidents. You do this by:
- With your capacitor disconnected from any power source, connect your discharge tool across the terminals.
- Hold it in place for a few seconds to ensure the capacitor is thoroughly discharged.
Setting the Multimeter
- Set the multimeter to 'resistance' or 'continuity' mode.
- Place the red probe on the capacitor's positive terminal, and the black probe on the negative terminal.
Reading the Multimeter
The multimeter reading will give an indication of the capacitor's health.
- If the multimeter displays a resistance, then decreases to zero and stays there, the capacitor is healthy.
- If the multimeter reading stays at zero, the capacitor has shorted out.
Testing Capacitors in Circuit
Testing capacitors in a circuit involves some specific techniques due to their connection with other components.
Identifying the Capacitor in the Circuit
The first step will involve identifying the capacitor in the circuit board. They can be recognized by the two terminals protruding from it, which are usually in highlighted colors for easy detection.
Disconnecting the Capacitor from the Circuit
It is recommended to disconnect at least one lead of the capacitor from the circuit to isolate it for testing. This is important to avoid false readings.
Capacitor Testing with an ESR Meter
Apart from a multimeter, an ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) meter can be used to test a capacitor in circuit. This device allows you to test the ESR of a capacitor, which basically measures how well the capacitor is performing its function of regulating current flow in the circuit.
- Connect the ESR meter probes to the capacitor's terminals.
- Ensure the ESR meter is set to 'capacitance' mode and observe the reading.

Frequently Asked Questions about How To Test A Capacitor
Can I test a capacitor while it is still attached to a circuit?
Generally, to get an accurate reading, you should disconnect at least one terminal of the capacitor from the circuit. This is because other components in the circuit can influence the readings. However, some advanced digital multimeters come equipped with the functionality to check the capacitors in-circuit, albeit only to check if it's completely dead.
What kind of multimeter should be used to test capacitors?
A digital multimeter that has a capacitance testing feature should be used for testing capacitors. Not all multimeters have this function, so it's paramount to ensure your multimeter has this feature before you use it to test a capacitor.
How should I handle a capacitor before testing it?
Capacitors can store electrical energy, even if the device is unplugged. Therefore, before testing, make sure you discharge the capacitor properly to avoid an electric shock. To safely discharge it, put on insulated gloves and use a resistor with a hook to connect the capacitor's terminals.
How accurate is a multimeter when testing capacitors?
While a digital multimeter is efficient in testing a capacitor, the range of capacitance it can measure may be limited and less accurate for small value capacitors. For comprehensive, accurate testing, especially for capacitors with small values, it would be ideal to use a capacitor tester.
Why does my multimeter show different readings for the same capacitor?
If your multimeter displays fluctuating readings for the same capacitor, several factors could be responsible. The capacitor may be malfunctioning, or your multimeter's capacitor testing functionality may not be accurate. Also, environmental elements like temperature and humidity can affect capacitor performance.
When should a capacitor be replaced?
If a capacitor is bulging, leaking, or shows signs of physical damage, it should be replaced immediately. Similarly, if a multimeter test indicates that the measured capacitance value is far from the manufacturer's specified value, replacement is recommended. Lastly, if the device the capacitor is in keeps malfunctioning, and everything else checks out, the capacitor could be the issue and should be exchanged.
Can a capacitor be repaired if it fails the test?
Generally, once a capacitor is damaged, it cannot be repaired and needs to be replaced. It's essential to replace it with one of the same or higher voltage rating and the same capacitance.
Is a specific Terminal to be connected to a multimeter while testing a capacitor?
When testing a capacitor with a multimeter, usually the red probe connects to the positive terminal and the black probe connects to the negative terminal of the capacitor. However, for non-polarized capacitors, you can connect to any terminal, as they don't have defined positive or negative terminals.

Pros of Testing a Capacitor
Ensures Safety
Lessens the Risk of Electric Shock
Testing a capacitor contributes to safety measures by helping to prevent electrical shocks, which can result in injuries or even fatalities. Capacitors store electrical energy and, if damaged or faulty, can release this energy unexpectedly. This can cause a shock to anyone handling the capacitor or any nearby equipment, particularly if the individual is not aware that the capacitor is still charged. Testing a capacitor can identify these risks before any harm occurs.
Prevents Fire Hazards
Faulty capacitors can also lead to a risk of fire. If a capacitor is malfunctioning, it can generate heat or sparks that can start a fire. This risk is particularly high in environments with flammable substances or materials. Conducting a test on a capacitor can detect any potential fire hazards so that they can be eliminated.
Enhances Performance and Efficiency
Detects Faulty Capacitors
Regular testing of a capacitor can detect issues such as a faulty or failing unit. This allows for the quick replacement or repair of the problematic capacitor before it can cause a complete system breakdown or failure. Thus, testing ensures that systems remain effective and running smoothly.
Optimizes Energy Use
Testing a capacitor can also ensure the device is functioning at its optimal level. By identifying capacitors that are not storing and releasing energy efficiently, these units can be fixed or replaced, ensuring better energy use and overall system efficiency. This results in economical operations and cost-effective energy management.
Longevity of Equipment
Increases Equipment Lifespan
Regular testing of capacitors can extend the lifespan of the equipment they are a part of. This is because a capacitor that is working effectively reduces strain and wear on other components, therefore extending the overall lifespan of the equipment.
Reduces Replacement and Maintenance Costs
When a capacitor is functioning properly, the chances of damage to connected components are significantly reduced. This lowers maintenance costs, as it results in fewer repairs and replacements needed.
Cons of Testing a Capacitor
Complexity and Risk of Handling
Requires Technical Knowledge
Testing a capacitor isn't a simple task. It requires a good understanding of electronics and equipment operation. Incorrectly testing a capacitor can lead to inaccuracies or even cause damage to the component.
Possibility of Electrical Shock
Despite precautions, there's an inherent risk of electrical shock when testing capacitors. As mentioned, capacitors store energy and, if not safely discharged prior to testing, can release this energy and cause harm.
Equipment Limitations
Requires Specific Testing Instruments
To accurately test a capacitor, you need specific testing equipment, such as a multimeter. Not everyone has access to this equipment, which can make the testing process more difficult and complicated.
Inaccuracies in Results
Even with the correct equipment, inaccuracies can still occur. This is especially true when dealing with digital estimations versus analog readings, leading to confusion and possible misinterpretation of results.
Time and Cost
Time Consuming Process
Testing each individual capacitor in a system can be time-consuming, especially in large and complex systems. Much of the time, this intricate work needs to be performed by an individual with specialized skills and training.
It Can Be Expensive
The cost of the testing equipment, as well as the potential cost of hiring a professional to conduct the testing if the user is not comfortable doing so, can be quite expensive. In some cases, it could be more cost-effective to simply replace a questionable capacitor rather than testing it.
Myths/Misconceptions About Testing a Capacitor
In the world of electronics, capacitors are common components. They store and deliver electrical energy in electronic circuits. Even so, there are many misunderstandings and misconceptions about testing a capacitor, often leading to wrong results and faulty appliances. This segment will debunk these myths to give you clarity about how to accurately test a capacitor.
Myth 1: The Multimetre Shows the Capacitor is Good
Many hobbyists and repair professionals rely on using a multimeter for testing a capacitor. A common misconception is that if the resistance of the capacitor increases slowly when it is tested with an ohmmeter, then the capacitor is functioning correctly. In other words, people believe that a multimeter can effectively test a capacitor.
Reality:
The truth is that an ohmmeter can only confirm whether a capacitor is completely dead (short or open) or not but it cannot verify if a capacitor is good. A capacitor can fail without presenting an open or short circuit. A multimeter's continuity test function can only tell three basic things, if the capacitor is entirely open, if it's completely shorted, or if it has some type of resistance.
Myth 2: All Bad Capacitors Bulge or Leak
There prevails a notion that bulging or leakage is the only way to identify a bad capacitor. It is often believed that if a capacitor doesn't show these symptoms, it is probably in a good state.
Reality:
While it's true that bulging or leaking capacitors are faulty, not all faulty capacitors will show these physical symptoms. Many capacitors may fail in other ways and still appear physically okay. Furthermore, there are failures that are undetectable without testing the capacitor in a circuit, under load.
Myth 3: Higher Voltage Ratings are Always Better
A common idea that people have is that replacing a capacitor with another of a higher voltage rating will upgrade the performance or longevity of the device.
Reality:
While a capacitor with a higher voltage rating can handle more electrical pressure, it does not mean that it will enhance the device's performance. In some cases, capacitors with higher voltage ratings can even be bigger in size, potentially leading to fitting issues in a compact circuit design.
Myth 4: Capacitors Withstand Any Polarization
There exists a misconception that polarization does not matter while testing a capacitor or replacing one in a circuit.
Reality:
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized, meaning they have a positive and negative pin. If they are installed in reverse, they can blow up or affect the functioning of the entire circuit. Non-polarized capacitors, however, can be inserted either way. Therefore, it is essential to note the polarization while testing or replacing electrolytic capacitors.
Myth 5: Capacity Determines the Capacitor's Quality
Some believe that the capacity (uf, mF or pF) of a capacitor directly relates to its quality, implying that a capacitor with higher capacity is automatically better.
Reality:
The capacity of a capacitor does not determine its quality, but rather its storage abilities. The capacitor's capacity must match the device's working condition; otherwise, it can lead to circuit malfunction. As for quality, it is determined by materials used, build construction and manufacturer's quality control.
Myth 6: All Capacitors Work the Same
This is the belief that all capacitors function the same way, regardless of their type.
Reality:
Different types of capacitors have different characteristics and are best suited for different applications. For example, ceramic capacitors are widely used in decoupling applications, while film capacitors are popular in audio circuits for their low distortion characteristics.
In conclusion, while it may seem straightforward, testing a capacitor is more complex than it appears, and it's filled with misconceptions. Understanding these myths and realities enhances your approach to testing and utilizing capacitors in various applications. Always remember, reliable knowledge and proper tools are your best friends when working with electronics.
Summary
At the end of the day, knowing how to test a capacitor is super important, especially for those who frequently deal with electronic devices. Whether you're using a multimeter or a capacitor tester, each method provides accurate results that can let you know if your capacitor is in good shape or needs to be replaced. This knowledge is crucial for maintaining your equipment and ensuring that you can make repairs whenever needed.
Understanding how to test a capacitor is definitely a lifesaver for DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike. It's a straightforward process that can save time, money and effort. The key is just to be cautious and patient. Regardless of the method, always remember that safety should be paramount. Keep this in mind and you'll surely get an accurate reading without any problem.
Life is easier when you know how to test a capacitor. Imagine the convenience of being able to identify issues with your capacitors early on. This knowledge not only helps you maintain the smooth operation of your devices but also lengthens their lifespan. So, don't take it for granted. Keep practicing your skills and become proficient at testing capacitors. You never know when you’ll need it!
About Sagan Electric
Sagan Electric is your go-to, friendly neighborhood electrical company right here in Sacramento, CA. We're not just some faceless corporation, we're part of the community. We ride the same streets, enjoy the same parks, and we're right here when you need us. With decades of experience under our belt, we've tackled everything from small domestic jobs right through to large-scale commercial projects. No job is too big or too small for our skilled and professional team. So, next time you're thinking electric, think Sagan Electric; your local Sacramento electric wizards.
Tags: capacitor testing, electronics, electrical engineering,








